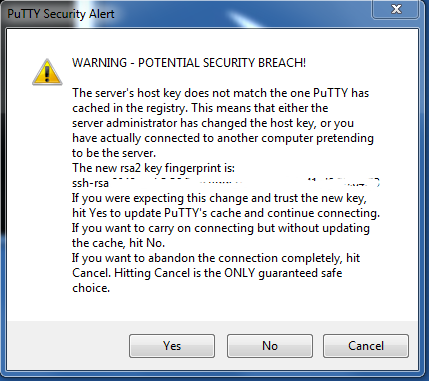
Introduction
Windows users at times may need to access UNIX/Linux functionality. For example they may need to move data from a data storage machine to a processing machine or to run particular software programs. The SSH client ‘PuTTY’ can be used for this, allowing you to securely connect your Windows computer with a remote Unix server of your choice. The instructions below outline how to both install and setup PuTTY.
Installing PuTTY
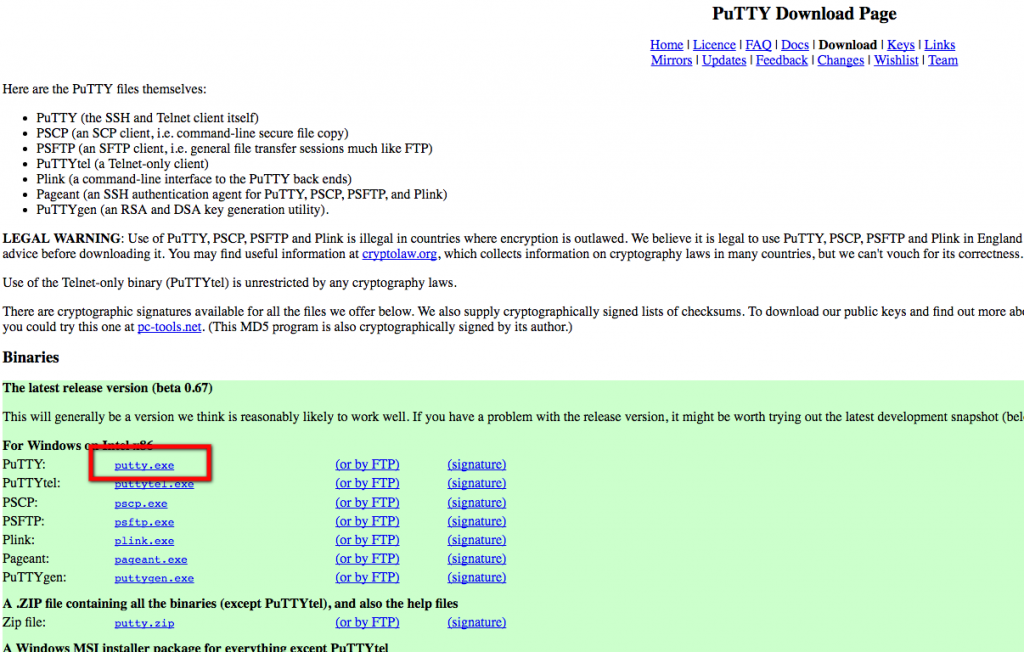
- Visit the putty homepage (http://www.putty.org) and follow the ‘Download putty’ page link.
- On the download page, click on the ‘putty.exe’ link to download the single file executable to your local computer (i.e. there is no installer file). Choose a suitable location for the download file.
Configuring a new connection
- Navigate to where putty.exe was downloaded to and double click on the putty icon to start PuTTY.
- The PuTTY main (session) window will open.
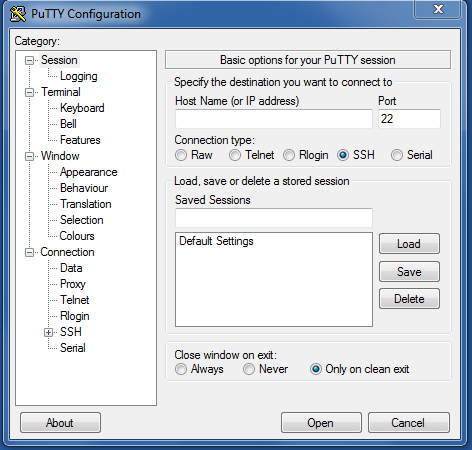
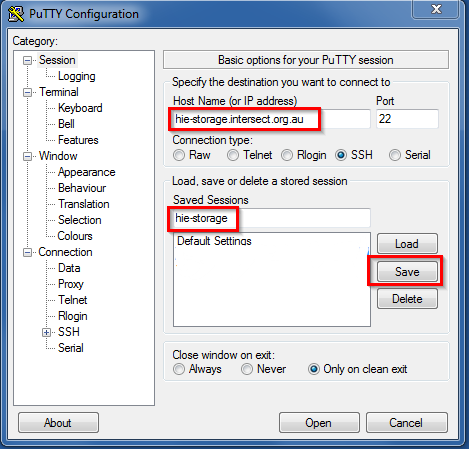
- In the ‘Host Name (or IP address)’ field, enter the name or IP address of the remote machine you want to access. In this example we will use the details of the ‘HIE-Storage’ machine, i.e. hie-storage.intersect.org.au. Enter a name in the ‘Saved Sessions’ box to refer to this connection (for future use) and then press the Save button.
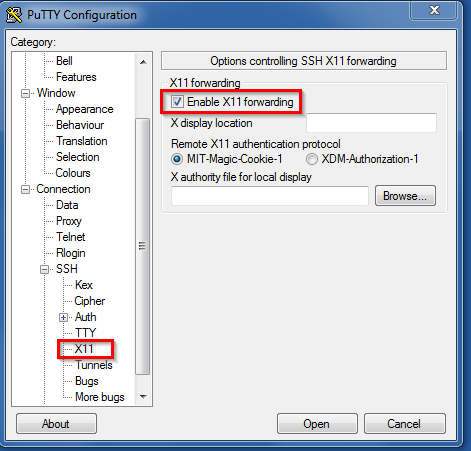
- Now, on the left pane, navigate to the Connection – SSH – X11 menu. Make sure that the ‘Enable X11 forwarding’ checkbox is ticked (this will enable graphical interfaces to programs).
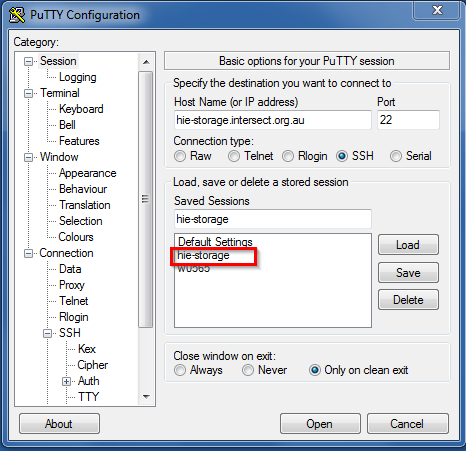
- Return to the main menu screen by selecting ‘Session’ on the left pane and click on ‘Save’ to save the changes (there should be an entry for your particular connection in the ‘Saved Sessions’ list). Any time you reopen PuTTY, you can click on your named connection in the list and click ‘Load’ to load in your saved settings.
- To open a connection to the remote machine, click on ‘Open’. This will now open an emulator window where you will be prompted for your username and password for that machine. Upon successful login you will now be presented with a Linux command line interface.